Stains
Intro
Stains can look nice sometimes; help to highlight various features depending on where the target is normally found in cell
- can be nuclear, membranous, both
- staining pattern, and also negative staining is important
- cyto = cytoplasmic, nuc = nuclear, mem = membranous
- fractions (ie 6/6) indicate % pos staining
34BE12 / CK903
(+) squamous epithelial (SCC/SCCIS [Bowen's dz]), basal cells, urothelial ca, metastatic breast ca, UDH breast, specific for prostate basal cells
- negative: prostate ca (though may stain basal cells?), DCIS breast
- "tonofilaments," epithelial cell intermediate filament HMWK (CK1-6 + CK9-20), forms dense networks resistant to stress
- has generally same staining characteristics as CK5/6
a1-antitrypsin
(+) Hepatocellular ca (1/2, hepPar more spec), normal hepto- + histiocytes, aat globules,
- neg:
- cytoplasmic
Alcian Blue (AB)
(+) sialomucins (salivary, sm and lg bowel), sulfamucins (lg bowel), hyaluronic acid (stromal myxoid mucin),
- neg: neutral mucin (prostate, gastric foveolar cells)
- staining is pH-dependent, nuclei are red/pink
Alpha-methylacyl-CoA-racemase (AMACR)
Enzyme involved in B-oxidation of branched-chain FA's, is significantly upregulated in prostate cancer
- ab's developed against its gene product (P504S protein), in dot-like and luminal fashion
- majority of prostate ca + for AMACR, sensitivity ranging from 82-100%
- AMACR expression may be dec in foamy gland, atrophic and pseudohyperplastic prostate cancers
- negative staining in small suspicious glands not necessarily diagnostic of b9 glands, and positivity also not diagnostic of malig glands (can be in mimickers of prostate ca)
AE1/AE3
(+) carcinomas, embryonal ca, yolk sac tumor, chorioca, teratoma, cholangioca, metastatic adenoca, Merkel cell ca, metastatic small cell ca
- negative: hepatocellular ca (HCC, up to 1/5+), RCC, high grade NE ca, adrenocortical cancers, glial/neuronal stuff, sex cord-stromal tumors (rarely +), dysgerminoma
- aka pan-cytokeratin cocktail, used in conjunction c CAM5.2, stains all basic (CK1-8) and some acidic (CK10, 11, 13-16, 19-20) epithelial cell intermediate filaments, this is a type of pan-CK (differentiated from sarcoma, melanoma, etc)
- can miss some HCCs b/c pan-CKs dont have CK18 (found in liver), which is why it is used c CAM5.2
a-FP
(+) hepatocellular ca (~1/2, not very specific, not fibrolamellar var), hepatoblastoma (better as serum marker), yolk sac tumor (also not specific), embryonal ca (not spec), liver in feti,
- neg: cholangioca (rare+), metastatic adenoca (var)
- cytoplasmic
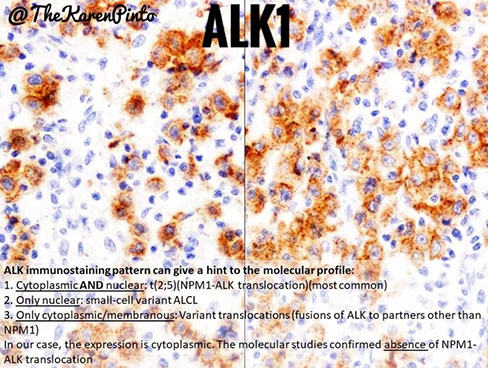
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)
(+) Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (~3/5, cyto), some neuronal cells, ALCL (t(2;5) ~4/5), lung adenoca c EML4-ALK rearrangement, stains as result of ALK translocations [ie t(2;5) NMP-ALK], DLBCL (rare)
- neg:
- nuc, cyto, membranous
Arginase-1
(+) hepatocellular ca, hepatocytes
- neg: cholangioca
- cyto
Auramine/Rhodamine
(+) acid fast bugs (better than Kinyoun, fluorescent red/yellow)
B72.3 (TAG 72)
IHC: (+) adenoca, secretory endometrium
- neg: mesothelioma
- cyto, mem
B-APP
Axonal spheroids
- occur c stretching and tearing (usually a result of angular acceleration / deceleration)
B-catenin
IHC: (+) Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm pancreas (SPN), sporadic tubular adenoma, fibromatosis (not superficial, only deep), primary vesical adenoca (10/10), colorectal ca (1/2+, nuclear staining), bladder ca (cytoplasmic), pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (cytoplasmic), pancreatoblastoma, juvenile nasal angiofibroma, adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma, fundic gland polyp (other FAP-assoc tumors), hepatoblastoma
- neg: pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, acinar cell ca / pancreatoblastoma (1/4+), Dysplasia Assoc Lesion or Mass (DALM), GIST
- nuclear staining, or can be cytoplasmic (bladder ca)
BCL1 (CyclinD1)
(+) cells undergoing division, epithelial (breast and colon) endothelial cells, (blastoid) MCL (nuclear), hairy cell leukemia and plasma cell myeloma
- nuc
B-cell Lymphoma 2 (BCL2)
(+) synovial sarcoma (3/3), solitary fibrous tumor, primary cutaneous mantle zone lymphoma, primary cutaneous DLBCL leg type, primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma (%+ dec c grade), CLL / SLL, MCL, MZL, endocervical metaplasia, BCC, Reactive LNs (T cells and mantle B cells are +)
- neg: reactive follicles (?), Burkitt's, endocervical adenoca,
- mem, cyto, normally inhibits apoptosis in centrocytes, turns off in germinal centers
B-cell Lymphoma 6 (BCL6)
(+) Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma, primary cutaneous DLBCL leg-type, germinal center cells (centroblasts and centrocytes), popcorn cells in LP-HL, cancerous T-cells in AITL, normal GC B cells, Burkitt
- neg: primary cutaneous mantle zone lymphoma; naive B cells, switched off in memory B cells and plasma cells,
- nuc; centrocytes switch off Bcl-6 due to IRF4/MUM1 regulation after interaction c CD23 and CD40L on T-cells to become memory B cells or plasma cells
-- BCL6 is expressed in germinal center centrocytes but not in naive B-cells, memory B-cells, or plasma cells
- BCL6 gene undergoes somatic mutation in the germinal center, but less frequently than IG genes
BCL-10
(+) Normal pancreatic acini and Acinar cell carcinoma (ACC) of pancreas (+ in >80%)
neg: Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (PanNET)
Ber-EP4
(+) adenocarcinomas (ie lung), sebaceous ca, epithelial cells, BCC
- negative: mesothelioma
- mem, good for use in body fluids bc mesothelial cells negative but BerEP4 highlights adenoca, mem
- stains ab to cell membrane glycoproteins on epithelial cells and carcinoma cells involved in cell adhesion
BF1
(+) subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTL), adult T-cell leukemia / lymphoma, aggressive epidermotrophic CD8+ Cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma, {rimary cuaneous CD4+ small/medium-sized T-cell lymphoma
b-hCG
(+) chorioca
Brachyury
(+) Chordoma
- neg: myxoid chondrosarcoma, myxopapillary ependymoma, chondroid meningioma
Brown and Brenn/Hopps
(+) Gram + (blue), Gram neg (red), nuclei (red), background (yellow)
Carbohydrate Antigen 19.9 (CA 19.9)
(+) Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
CA-125
(+) lots of cells (not very spec for ovarian ca by IHC, better as serum marker monitoring ovarian ca recurrence)
- luminal
calcitonin
(+) thyroid (medullary ca, not spec), thyroid C cells, NE tumors
- cyto, extracellular
caldesmin (h-caldesmon)
(+) smooth muscle tumors (LM, LMS), glomus tumor
- negative: myofibroblasts, endometrial stromal tumors of the uterus, UTROSCT, fibromatosis, nodular fasciitis
- smooth muscle marker, cyto
calponin
(+) ME cells breast, smooth muscle (vessels), myofibroblasts (var), glomus tumor, nodular fasciitis, similar to a-actin)
- negative:
- contractile-apparatus assoc proteins, cyto
calretinin
(+) mesothelioma, sex cord stromal tumors, adenomatoid tumor, UTROSCT (most sens), cardiac myxoma, adrenocortical tumors, neural + epithelial cells
- neg: serous ca, sm muscle tumors of uterus (LM, LMS), endometrial stromal tumors of the uterus (endometrial stromal sarcoma), adenoca
- nuc, cyto
CAM5.2
(+) Paget's dz, HCC, NE carcinomas, focal pos aberrant expression in high-grade melanomas, MPNST, leiomyosarcoma, embryonal ca, yolk sac tumor, chorioca, teratoma, papillary and follicular ca thyroid, anaplastic ca thyroid (var), medullary ca thyroid, parathyroid ca, hepatocellular ca, chooangioca, metastatic adenoca, Merkel cell ca, metastatic small cell ca
- negative: SCCIS (Bowen's dz), SCC, glial/neuronal/nerve sheath stuff, sex cord-stromal tumors, dysgerminoma
- cyto, "non-squamous / simple keratins," stains epithelial cell intermediate filaments LMWKs (CK7-8 + CK18-20) in simple-non-squamous keratins distributed in cytoplasm and doesn't bundle so found in organs where there isn't much stress (colon, liver, prostate, kidney)
- used in conjunction c AE1/AE3
- can detect HCCs bc has CK18 (found in liver)
- may miss some cases of SCC (which is predominantly HMWKs), also can stain some non-carcinomas (melanomas, MPNST, etc)
Calmodulin binding transcription activator 1 (CAMTA1)
Carbonic Anhydrase (CAIX)
(+) Clear cell RCC (very sens and spec), focal positivity in necrotic areas of other tumors (papillary RCC)
- neg:
- mem, made from vHL mutations, which regulate Hypoxia Inducible Factor (HIF) and causes HIF increase and thus increase CAIX and VEGF, thus found in ischemic tissues
-- clear cell ca can be treated c Sunitinib, so it's important to correctly dx
cathepsin-K
(+) PEComa, osteoclasts, Xp11 RCC, chordoma
- neg:
- cyto
Clusters of Differentiation (CD) markers
The polyclonal antibodies against the nuclear antigen terminal deoxynucleotridyl transferase (TdT) and towards CALLA were the first breakthroughs in immunophenotyping
- George Kohler made homogenous antibodies against sheep RBCs
- the fusion of B-cells from the spleens of animals (usually mice) with non-secreting myeloma lines allowed the production of large amounts of monoclonal antibodies
- Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens (HDLA) workshops made rules that once two different labs independently made the same molecule
- Clusters of Differentiation (CDs) were determined by statistical methods from these molecules [1]
CD1a
(+) - Langerhans cell histiocytosis (c anti-S-100; pretty specific), cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, myeloid leukemia, Papillary thyroid carcinoma, T-ALL, thymoma (+TdT/CD99), cortical thymocytes, immature dendritic cells (CD86-), Langerhans cells (CD86+)
- neg: B-cells, follicular dendritic lymphomas, Erdheim-Chester disease
Family (types a-e) of MHC-I molecules on surface of APCs (assoc c beta-2 microglobulin) that present to T-cells - thus stains membranous
- TB, Leishmania donovani, and malignant melanoma may escape immunodetection by downregulating CD1
CD2
(+) One of the earliest T-cell restricted markers, 95% of thymocytes, NK-cells, T-cell and NK-cell cancers, systemic mastocytosis
- neg: B-cells (rarely is aberrantly expressed)
- mem, binds CD58 on APCs, inducing co-stimulatory signals that promote homing and epithelial adhesion; E rosette receptor
CD3
(+) Used to detect T-cells and NK cells in benign and malignant conditions, anti-CD3 ab's used to tx graft rejection
- neg: aberrantly lost in ALCL, some mycosis fungoides, and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
- cyto and mem, cytplasmic marker used by FC only, most specific T-cell marker (found on mature T cells), made of gamma, delta and sigma chains; assoc c TCR
CD4
(+) T-helper cells (lots of T cell neoplasms in general), dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, Langerhans cells, receptor for HIV (serum levels used to monitor HIV progression)
- mem, normal CD4:8 ratio is 2-6:1; double neg or pos outside thymus probably neoplastic
- stains membranous
CD5
(+) normal and cancerous T-cells, expression in B-cells suggests cancer (mantle zone lymphoma), thymic carcinoma (in epithelial cells), but not thymoma (stains lymphs but not epithelium, vs CD1a), CLL/SLL, MCL, blastoid MCL, DLBCL (rare)
- neg: NK cells, normal Naive B cells that circulate in PB and are in primary lymph follicles and the mantle zone of follicles, thus negative in primary cutaneous MZL and FCL, aberrant CD5 loss seen in peripheral T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides)
- membranous
- CD19/20/5 (+) B-cells common in RA
CD7
(+) T-ALL (strong); aberrant expression in AML (assoc c poor px; can be used to follow dz/tx); NK cells
- neg: aberrant loss inc T cell ca, stays positive in reactive conditions
- mem, first CD marker to appear in T-cells (even before CD2), also seen in NK cells, plays role in T-cell development, found on all T cells
CD8
(+) Cytotoxic and suppressor T-cells, and cancerous NK cells, circulating CD4+/8+ cells likely cancerous, splenic hamartoma
- neg: hemangioma or littoral cell angioma
- is a transmembrane receptor protein that acts as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR), helping with antigen recognition and strengthening the TCR-antigen interaction by MHC-I molecules
CD9
Not used by patologists ...
But is a cell surface protein that mediates cell adhesion
CD10
(+) B cells in germinal center, precursor B (hematogones), some immature T cells, normal mature neutrophils, Burkitt + follicular lymphoma, and B/T cell lymphoblastic lymphomas (B-ALL), primary cutaneous Follicle center lymphoma (though negative if has diffuse histology), neoplastic plasma cells,
In non-heme tissues:
(+) liver/bile canaliculi in hepatoceullular ca, ME cells of breast, endometrial stroma (stromal sarcoma), sex cord stromal tumors, metastatic adenoca's, endometriosis, glomerular epithelial cells and brush border of proximal tubules (and thus in RCC); pancreatic solid-pseudopapllary neoplasm, atypical fibroxanthoma; HCC
- neg: cholangiocarcinoma, primary cutaneous MZL, primary cutamepis DLBCL leg type, melanoma, sarcoma, sarcomatoid carcinoma of skin
- mem, aka Common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA)
- good for childhood and B-cell lymphoma characterization
CD11
CD11a
alpha-integrin that binds CD18 and regulates cellular adhesion
- deficiency may be used in FC as a marker of APL (although tx induces CD11a expression) or AML
CD11b (aka MAC-1)
(+) Hairy Cell Leukemia (HCL), acute agranulocytosis (CD11b+, CD117-), monocytes, granulocytes, NK cells
- neg: APL (CD11b-, CD117+)
- mem, flow marker of T-cell activation and of NK-cells
CD11c
- aka C3r
(+) histiocytes, NK-cells, 50% B/T cells, Hairy Cell (HCL), grans, weakly expressed in CLL/SLL
(-) in MCL and MZL
- mem, used in flow, important in monocyte adhesion
CD13
(+) Myeloid cells (though CD33 more specific), AML (myeloid leukemias)
- can be weak in ALL, transient myeloprolif disorders
- flow marker
- receptor for coronavirus and mediates CMV infx
CD14
Stains mature monocytes and macrophages
- may also be (+) in Langerhans/dendritic cells and B cells
(+) in AML M4/5, CMML, and histiocytic sarcoma; but is (-) in myeloid precursor lesions (AML 0-3,6/7)
CD15
- aka Leu-M1
(+) RS cells in classic Hodgkins lymphoma, AML c differentiation, adenoca, EBV infx can have CD15 (+) RS-like cells, granulocytes, mature monos
In lymph nodes, may stain virally infected cells (CMV), and some T-cell lymphomas
- neg: ALCL, mesothelioma
- cyto and golgi (perinuclear dot-like), aka LeuM1, Carbohydrate (not protein)
CD16
Fc gamma receptor; Stains normal and neoplastic NK cells, lymphocytes, and granulocytes
- Used as preincubation c CD32 sometimes to prevent nonspecific binding
- may help to sub-classify lymphomas
CD18
May be deficient in LAD type 1, but is generally not used by patologists
CD19
(+) B-cell marker, from pre-B cell stage onward, hematogones of BM, remains (+) in DLBCL after Rituximab tx (vs CD20), some myeloblasts in AML c t(8;21)(q22;q22)
- neg: in plasma cells (and myelomas), mast cells
- May be more sensitive than CD20 in detecting B-cell disorders
- CD79 will also remain (+) after tx in DLBCL
CD20
(+) Expressed after CD19/10 but before CD21/22 and stays on B-cells until they develop into plasma cells, 80% of NLPHL and 20% CHL (poor px), CLL/SLL (dim)
- Expression lost after Rituximab tx (vs CD19)
- closely related to FMC-7, which recognizes a special CD20 arrangement; tends to stain the same as CD20
- Not useful to for BM involvement of DLBCL
- neg plasma cells, HL (+ in 1/5)
CD21
(+) in dendritic cells (along c CD23/35), splenic littoral cell angioma
- neg: splenic hamartoma
- Receptor for EBV and HHV8, and (+) in B-cells (particularly marginal and mantle cells)
- Used to dx follicular dendritic cell sarcoma and look at network of denritic cells in various lymphomas (FL,MCL, NLPHL)
CD22
(+) HCL; aberrant expression useful to detect monoclonal B cells of CLL admixed with benign polyclonal B cells
- Last antigen acquired in B cell maturation, binds to CD75
CD23
(+) CLL/SLL , dendritic cell network in lymphomas (FL, MCL, AITL, NLP-HL)
- neg: MCL (may be dimly [+])
- B-cell growth factor that helps differentiation into plasma cells, and an IgE receptor
CD24
Promotes prolif of B-cells and stops differentiation into plasma cells
- Strong expression in some cancers (ie breast and GI) may bode a poor px
CD25
(+) HCL (though CD103/123 may be better), ALCL, normal /neoplastic mast cells ( clusters of >15 cells in BM involvement of SM, diagnostic of SM if clusters found in GI biopsy, called Urticaria Pigmentosa if in a skin biopsy), activated lymphs, HCL
-elevated serum values in pts with HTLV-related ATCL
- IL-2 receptor
- indicated clonality and KIT rearrangement in mast cells
CD26
Not used by patologists, but is a costimulatory molecule for T-cells
CD27
Not used by patologists
- Marker for B/T cells and binds CD70
CD28
Not used by patologists, but plays important in CD4+ T cell activation, IL2 production and T helper 2 development
CD29
Not used by patologists, but monitors cell adhesion
CD30
- aka Ki-1; Ber-H2; was originally developed against RS cells and large neoplastic cells (know now as ALCL) [2]
- may be targeted with Brentuximab vedotin
- cell surface cytokine receptor that is part of the TNF receptor superfamily 8; binds CD30L activating the NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway resulting in cell prolif or apoptosis;
- first found on Reed-Sternberg (RS) cells
In lymph nodes, stains activated lymphoid cells as well as RS cells
(+) immunoblasts (like viral [EBV] lymphadenopathy), NK cells, Reed-Sternberg cells (cHL), ALCL (has targetoid membrane and Golgi appearance), embryonal carcinoma ([+] in a few seminomas), MF (positivity suggests transformation), other lymphomas, activated T and B cells, plasma cells; PMBL
[-] in NLPHL, circulating mature B and T cells,
CD31
(+) Most sens/spec endothelial marker (better than CD34), vascular lesions (Kaposi sarcoma, angiosarcoma) [D2-40 may be better at detecting invasion], Mgkc's, macrophages
- cyto, mem, aka PECAM1, helps leukocyte migration
CD32
Receptor for the Fc region of IgG
- but not used by patologists
CD33
Myeloid marker used to detect myeloid/monocytic leukemias
CD34
(+) Human hematopoietic progenitor cells AKA pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) AKA blasts; immature mesenchymal cells (fibroblasts); normal (esp proliferative) and neoplastic endothelial cells, GIST (most epithelioid cell neoplasms +), DFSP, Kaposi sarcoma, epithelioid sarcoma, hemangiopericytoma, chloromas, angiosarcoma (most spindle cell tumors), solitary fibrous tumors (SFT), HCC, nerve sheath tumors; NUT midline tumor (1/2+)
- neg: fibromatosis, leiomyosarcoma, dermatofibroma, endometrial stromal sarcoma, desmoplastic mesothelioma, synovial sarcoma, carcinomas, melanoma, lymphoma (except ALL)
- cyto, mem
- may be used in cord blood during autologous or allogeneic stem cells transplantation to count HSCs
CD35
(+) in dendritic cells c CD21, thus can dx follicular dendritic cell sarcoma and attempt to highlight networks of dendritic cells
CD36
Lots of functions (scavenger receptor) that can stain a variety of cells from multiple systems
- patologist use is uncertain
CD37
Inhibits IgA responses, but not patologist use as of yet
CD38
(+) granulocytic precursors, monocytes, some natural killer (NK) cells, plasma cells, activated T-cells, myeloma, leukemic blasts of any lineage
- bodes poor px if (+) in CLL (when >30%+), indicating IgVH nonmutated status and more aggressive course
Normally CD138 is a ribosyltransferase absent on most immature hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), though appears at early stages of differentiation [1]
CD39
No use for patologists, but is an endothelial ATPase that blocks platelet activation
CD40
not significantly used by pathologists, but may have some px value in soft tissue sarcomas and DLBCL
CD41
(+) Normal and cancerous Mgkcs and platelets
- Dx AML-M7 (Mgkc differentiation) and Glanzmann thrombasthenia
CD42
(+) Normal and cancerous Mgkcs and platelets
- part of GPIb/V/IX complex on plt cell surface, which is a receptor for vWF
- Dx AML-M7 (Mgkc differentiation)
CD43
(+) Normal and cancerous T cells, 70-90% of T-cell lymphomas; myeloid sarcoma (chloroma, more sens than CD45 ), aberrant B cell expression in MCL, SLL, and MZL (not usually in FCL), B-cell lymphomas, pulmonary MALT lymphoma (CD20/43+ )
- neg: lymphoid hyperplasia, reactive B cells, under-expressed in Wiscott-Aldrich syndrome; FCL
- (+) CD4+/56+ hematodermic neoplasm / Plasmacytoid dendritic cell tumor(?)
CD44
(+) non-neoplastic (b9 / reactive) urothelial cell changes (+ in basal layer), small cell ca of prostate
- neg: urothelial transitional cell CIS (- or dim)
- mem
CD45
(+) (Almost) all normal and cancerous leukocytes, good to see if an unknown tumor is lymphoid
- grans have intermediate expression and erythrocytes very low expression; dim CD45 assoc c plasma cells
- neg: nucleated RBCs, some plasma cells, Reed-Sternberg cells (except in NLPHD), lymphoblastic lymphoma (var), anaplstic large cell lymphoma (var), follicular dendritic cell neoplasm (var), myeloid sarcoma, and weak / absent in myeloblasts
- cyto, mem, aka Leukocyte common antigen (LCA), used as a "gating" parameter on flow cytometry; aka PTP receptor type C (PTPRC)
CD45 RA
- found on naive and activated B- and T- lymphocytes
(+) CD4+/56+ hematodermic neoplasm / Plasmacytoid dendritic cell tumor, aggressive epidermotrophic CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma
CD45 RO
- appears after T-cells encounter antigen; found on memory cells
aggressive epidermotrophic CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma
CD46
No use for patologists, but helps downregulate immune system
CD47
Differentiate T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (+) from T-lymphoblastic lymphoma (-)
CD52
(+) in eos vs neutros (-)
- May be used to tx some malignancies
CD54
aka ICAM-1 (ligand for LFA-1 [CD50])
CD55
aka Delay Acceleration Factor (DAF); used to dx PNH
CD56
(+) Normal and cancerous NK cells, large granular lymphs, neuroendocrine cells, small cell ca, Schwann cells, medullary ca thyroid, parathyroid ca's, plasma cell tumors, plasma cell tumors, small cell carcinomas, neuroendocrine marker (not very specific)
- neg plasmablastic lymphoma
- mem, aka Neural-Cell Adhesion Molecule (N-CAM), regulates neuron-neuron and neuron-muscle interactions
CD57
(+) Schwann cells, NE cells, carcinoid, subset of normal and cancerous NK cells, stains rosettes around L&H cells in NLPHL, high grade prostatic adenocarcinoma, metanephric adenoma
- neg: DLBCL and CHL, high grade urothelial carcinoma
aka Leu-7
CD58
Nonspecific, used to assess aberrant INTENSITY of expression
- may detect MRD in pre-B ALL
CD59
Present on every cell in human body
- Decreased (with CD 55-DAF) in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)
CD61
aka ITGB3, is the human integrin beta chain beta 3 protein, highlighting glycoprotein IIIa on platelets
- (integrins participate in cell adhesion and cell-surface mediated signaling)
- Normal and cancerous megakaryocytes and platelets
- may distinguish TTP (+ platelet rich thrombi) from DIC (-)
(+) in megakaryocytic (M7) AML
CD62
aka Selectin E; Not used by patologists
CD63
marker for melanoma (non-specific) and stains 100% of angiomyolipos and breast carcinomas
- Not generally used
CD64
Stains monocytes and may predict infection in several specific scenarios (newborns, RA pts)
CD65
Myeloid marker used in FC
CD66
expression (of CD66a) may predict mets in melanoma
CD67
aka 66b
marker for myeloid cells
CD68
(+) lysosomes in histiocytes and histiocytic tumors, monos/macros, basophils, dendritic cells and fibroblasts, myeloid sarcoma (AML c monocytic diff)
- cyto, mem
CD70
May help differentiate thymic ca (+) vs thymoma (-)
CD71
(+) used in flow to identify AMLs c erythroid (M6) or Mgkc (M7) differentiation, aggressive CD10-pos B-cell lymphomas
- neg: indolent CD10-pos B-cell lymphoma
- aka transferrin receptor (on erythroid cells [nonspecific])
CD72
B-cell marker (not really used)
CD74
aka MHC II assoc invariant chain
- prevents the premature binding of new MHC II proteins with endogenous proteins
- Expressed on many APCs and stains germinal center lymphocytes and B-cell (but only rarely T-cell) lymphomas
CD75
Not really used, but can id RS cells and follicular center cell lymphomas
CD77
Can id germ center cells
CD79a
(+) Normal and cancerous B cells and plasma cells (broader than CD20), T-ALL (var)
- neg RS cells
-complements CD20 (stains similar cells), but stains more cases of plasma cell myeloma
- can differentiate pre-B lymphoblastic lymphoma from Ewing's sarcoma
CD99
(+) peripheral neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs) / Ewing sarcoma (not spec, has distinct membranous staining in these tumors), other small round blue cell tumors of childhood, T lymphoblastic lymphoma, granulosa cell tumors, (poorly diff) synovial sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, solitary fibrous tumors (SFT), and mesenchymal chondrosarcoma, , small cell osteosarcoma, sex cord stromal tumors, many others
- always negative in neuroblastoma
- mem (more spec), cyto, aka p30/32, mic-2, O-13, o
CD103
(+) Sensitive and specific for HCL, but also enteropathy-assoc T-cell lymphoma and some cases of MZL of spleen, intestinal epithelial T-cells
- cyto
CD105
aka Endoglin
- Receptor for transforming growth factor B1
- highly expressed on endothelial cells during tumor angiogenesis and inflam, but only weakly or negatively stains vascular endothelium of normal tissues
- More sensitive and specific marker for tumor angiogenesis than anti-CD31 (labels newly formed blood vessels)
CD117
aka c-kit (***C-kit-gastriC-C-kit***)
- tyrosine kinase with gene on 4q12, adjacent to PDGFRA
- made by cells of Cajal (precursor to GISTs)
- good for differentiating GISTs from Kaposi's, Schwannomas, and smooth muscle tumors
- melanocytes (esp junctional; up to 40% of melanomas)
- seminomas (membranous)
- progenitor myeloid cells (AML/CML)
- in BM: mast cells (mastocytoma), precursor cells (pronormoblasts, myeloblasts, promyelocytes)
- PEComa
- Thymic carcinoma (+) vs thymoma (-)
CD123
(+) CD4+/56+ hematodermic neoplasm / Plasmacytoid dendritic cell tumor, hairy cell leukemia (variable in the variant form of HCL)
CD133
Good candidate for stem cell marker of many lineages, and is seen on several types of cancer cells, and is suspected to be involved with cancer mets [1]
CD138
(+) Plasma cells (normal and cancerous), very specific within heme realm, but also stains wide range of epithelial and mesenchymal neoplasms
- loss of CD138 assoc c aggressive SCC
- mem, aka Syndecan 1, protein encoded by a transmembrane (type I) heparan sulfate proteoglycan gene; is expressed in the late stages of B-cell differentiation when almost a plasma cell and moderates neovascularization through binding fibroblast growth factor
CD141
aka Thrombomodulin
- Mesothelioma (+) vs lung adenoca (neg, must exclude vasculature)
(+) in urothelial ca, endothelial cells
SCC (+)
CD146
(+) in melanoma, choriocarcioma (in intermediate trophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts), exaggerated placental site, placental site trophoblastic tumor, leiomyosarcoma, clear cell sarcoma, mesothelioma, smooth muscle
- neg: reactive mesothelium, placental site nodule (var), epithelioid trophoblastic tumor (var)
- mem, aka Melanoma Cell Adhesion Molecule (MelCAM)
CD163
(+) monocytes (+) and tissue macrophages (+++), histiocytic sarcoma
- mem, acute phase-regulated transmembrane protein that mediates the endocytosis of haptoglobin-hemoglobin complexes and as an anti-inflammatory signal
CD164
aka MUltiglycosylated Core protein 24 (MUC24); it is similar to CD34, being expressed on stem cells and progenitor cells
- can be seen in Sezary syndrome malignant T-cells or on basophils upon allergen recognition
CD207
(+) Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH)
- neg: indeterminate cell histiocytosis, Rosai-Dorfman dz,
CDX2
(+) small and large intestines, ca's c GI phenotype, mucinous BAC/adenoca [focal, bladder adenoca) (var), adenoca of urinary bladder, mucinous ca ovary, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) pancreas, extrahepatic bile duct ca's (1/3), appendiceal carcinoid, yolk sac tumor (2/5+), morules (endometrial)
- neg: PanIN; squamous metaplasia (endometrium)
- nuc
CEA
(+) in some but not all carcinomas, colon, HCC, colorectal ca, stomach, lung adenoca, pancreatobiliary, breast, urothelial, cervix
- negative: kidney, adrenal, prostate, mesothelioma, ovary, endometrium
- the cancer is a carcinoma if CEA pos, but if CEA neg does not exclude carcinoma
mCEA
(+) cholangioca, metastatic adenoca to liver,
- neg: hepatocellualr ca
pCEA
(+) hepatocellular ca (8/10, canalicular, pretty spec), cholangio ca (cytoplasmic), metastatic adenoca to liver (cytoplasmic)
CgA
(+) Carcinoid (10/1)
- neg:
Chromogranin A (CHR)
(+) neuroendocrine, pheochromocytoma, carcinoid, small cell ca, Merkel cell ca, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor / islet cell tumor, neuronal, medullary ca thyroid, parathyroid ca's,
- negative:
- more specific than SYN for NE, cytoplasmic (granules)
c-kit
(+) GISTS, chromophobe RCC, var oncocytoma, epithelium in thymic carcinoma, PEComa, dysgerminoma, mast cell neoplasms, melanoma (2/5+), sclerosing mesenteritis, salivary tumors c epithelial /myoepithelial part (stains luminal epithelium), blasts in myeloid leukemia
- negative: CCRCC and papillary RCC, non-thymic ca (var), thymoma, embryonal ca, yolk sac tumor, chorioca, Kaposi's, Schwannomas, and smooth muscle tumors (leiomyoma)
- cyto, mem, aka CD117 marker for tx response in CML and GISTs (better predictor than IHC), tyrosine kinase with gene on 4q12, adjacent to PDGFRA, made by cells of Cajal (precursor to GISTs)
Claudin-1
(+) Perineurioma
Clusterin
(+) follicular dendritic cells / neoplasms, tenosynovial giant cell tumors, pancreatic NE tumors, lots of others!!!; ALCL (golgi pattern), MGKC (strong cytoplasmic)
- cyto
Congo Red
(+) amyloid
Crystal violet
(+) amyloid
Cyclin D1 (Bcl-1)
(+) cells undergoing division, endothelial cells, (blastoid) MCL
- nuc
- normally functions as a protein that allows progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle (accumulates in nucleus) and degrades during the S phase
-- mediated by the Ras pathway
- in mantle cell lymphoma cyclin D1 is translocated to the IgH promoted, leading to cyclin D1 overexpression
Cyclin E
(+) Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor
- neg: placental site nodule
Cytokeratins
Intermediate filaments (similar to GRAP, vimentin, neurofilament, and desmin), epithelial markers,
- Carcinoma markers, can be used to detect micromets in breast ca
- classified based on gel-electrophoresis pattern, 1-8 are basic and 9-20 acidic (nearly the exact opposite of the pH scale...)
- the last 2 basic (7+8) and acidic (19+20) CKs are low molecular weight bc move further on gel
- thus HMWKs (ie CK5/6 stain) = CK1-6 + CK9-17
- LMWK (ie Cam5.2) = CK7-8 + CK18-20
- also, AE3 stains basic CKs (1-8) and AE1 stains acidic (9-20) CKs
--- caveat: some non-carcinomas may be positive for cytokeratins (synovial sarc, epithelioid angiosarc)
- peri-nuclear dot pattern in NE ca's (stains epithelial NE ca's [carcinoid, , not the neural or non-epithelial ca's [pheo, paraganglioma, neuroblastoma])
(+) non-seminomatous germ cell tumors (generally neg in seminoma), Wilms, some PNETs, small cell ca, Merkel ca ca, desmoplastic small round cell tumor
- neglymphomas, neuroblastoma, small cell osteosarcoma, Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma
CK5/6
(+) squamous epithelial (SCC), basal cells, urothelial cell ca, ALH/LCIS and UDH, metastatic breast cancer
- negative: prostate ca, ADH/DCIS
- "tonofilaments," epithelial cell intermediate filament HMWK (CK1-6 + CK9-20), forms dense networks resistant to stress
CK7 and CK20
(+) CK7 = above diaphragm (lung, breast, salivary glands, thyroid) and female gyn (uterus [endometrium] and ovary [non-mucinous]), also mesothelioma
*** 7th "heavin" - breast and female stuff, "heaving" lungs***
(+) CK20 = below the diaphragm (colorectal) and Merkel cell ca (dot-like perinuclear pattern), gastric cardia (CK7 neg), pos in umbrella cells only in b9 / reactive urothelial atypia and pos in all cell layers in urothelial CIS
- neg: metastatic small cell ca
** 20 is the shits, kinda looks like a toilet...***
(+) CK7 and CK20 = stuff that contributes / feeds directly into the shits (pancreas, stomach, bile ducts) and piss (urothelium)
- pos in Barrett's (CK7 surface and deep, CK20 surface only), cholangioca
negative CK7 and CK20 = another level removed from the shits (liver) and piss (kidneys, prostate) and also neuroendocrine cells
- aka simple viscera
- hepatocellular ca also usally CK7/20 neg
CK19
(+) Cholangioca
CK903
*** Prostate Panel: p63, CK903, Racemase)***
- basal cells (p63+ nucleus, CK903+ cytoplasm) present in b9/non-invasive lesions, absent if invades and acinar cells are Racemase negative in b9 and pos (cytoplasmic) if invasive
(+) cholangioca, SCC lung, mesothelioma
- neg: hepatocellular ca, non-mucinous adenoca lung, mucinous adenoca lung (var), small cell ca lung, carcinoid lung,
D2-40 (Podoplatin)
(+) (lymphatic) endothelium, mesothelium (mesothelioma), seminoma (10/10), dysgerminoma, embryonal ca (1/3), adrenocortical neoplasms, myxoid chondrosarcoma, myxopapillary ependymoma (var), nerve sheath tumors, follicular dendritic cells/tumors
- negative: RCC, teratoma, chorioca, spermatocytic seminoma, embryonal ca (var), yolk sac tumor
- membranous
Das-1
(+) esophagus (Barrett's mucosa)
- neg: gastric cardia (intestinal metaplasia of the gastric cardia)
Desmin
(+) skeletal muscle tumors (sensitive but not specific), smooth muscle, myofibroblasts (variable) (nodular fasciitis, fibromatosis), rhabdomyosarcoma, blastema of Wilms tumor, desmoplastic small round cell tumor, smooth muscle spindle cell tumors (LM, LMS, RMS), reactive mesothelium,
- negative: PNET, neuroblastoma, Merkel cell, small cell, lymphomas, mesothelioma, glomus tumor
- intermediate filament, universal muscle marker
Diff Quick
(+) nuclei (blue), cyto (pink), H pylori (dark blue)
DOG1
IHC: (+) GIST
DPC4
- loses expression in 1/2 of pancreatic adenoca's and some colonic adenoca's
E-cadherin (CAD-E)
- (+) membranous, ductal and lobular cells of breast (and ductal ca), pos in all layers of normal / reactive urothelium, specific marker for erythroid differentiation
- negative: lobular ca InSitu [LCIS] (classic loss), Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia (ALH) + invasive, urothelial CIS
- p120 (an E-cadherin-bp) can also be used in breast ca differentiation (membranous in DCIS, LCIS is cytoplasmic)
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)
- validated only for met coloractal ca, need >1% positive (partial/complete) membranous staining to call pos, also positive in 91% of metastatic breast ca (Triple Negative Brast Carcinomas) which can be helpful if the usual markers are negative
- used to see if can treat c cetuximab or panitumumab which is best predicted c KRAS mutation status (rather than the strength of EGFR positivity)
Epithelial Membrane Antigen (EMA)
- aka MUC1
(+) meningioma, myelomas, Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), popcorn cell in Hodgkin lymphoma, RCC, MPNST (focally), synovial sarc, spindle cell ca's, chorioca (1/2), teratoma, cholangioca, metastatic adenoca, mesothelioma, adenomatoid tumor, endometrioid ca, struma ovarii, carcinoid (var), PEL, low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma, solitary fibrous tumor (SFT), perineurioma
- negative: hepatocellular ca, adrenocortical neoplasms, thyroid, NE tumors, non-seminoma germ cell tumors, conventional and spermatocytic seminoma, reactive mesothelium, choroid plexus tumors, myxoid chondrosarcoma, myxopapillary ependymoma, sex cord-stromal tumors, sertoli cell / granulosa cell tumors
- epithelial marker, used as a CK-helper, usually stains the same except for some of the above tumors
EpCam
(+) Chomophobe RCC (diffuse), var oncocytoma and CCRCC
-
ER
(+) breast (1/2) [normal, cancerous, metastatic, ovarian, endometrial], highest expression in endometrioid carcinoma (>9/10), low in serous ca (1/2 of cases), endometriosis (glands and stromal pos)
- negative: pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm (both are PR pos), HPV-assoc adenoca, mesothelioma
- used to monitor tx (tamoxifen) in breast ca
- ER controls PR (ER-/PR+ probably false, ER+/PR- is uncommon)
- nuclear, positivity in breast ca is weakly prognostically better bc can be tx'd c tamox
ETS-related gene (ERG)
(+) Epithelioid sarcoma (60%), epitheioid hemangioma, epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE), Ewing sarcoma (5-10%), prostate AC, a small subset of AML,
factor VIII
(+) endothelial cells, dermatofibroma, hepatocellular ca (sinusoidal capillarization)
- negative: DFSP, b9 liver nodules
Fascin
(+) RS cells and dendritic reticulum cells
Feulgen
(+) microbial DNA of acid-fasts bugs magenta, used in ploidy studies, nuclei (magenta), background (green)
Fite
(+) delicate acid-fast bugs (M leprae, Nocardia, red)
Friend leukemia integration 1 factor (FLI1)
(+) epithelioid sarcoma (in 70%), epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, (EHE), endothelium (blood vessels, lymphatics), Ewing sarcoma, subsets of a wide range of mesenchymal tumors, subsets of high-grade lymphomas (lymphoblastic lymphomas, ALCL, and AITL) and DLBCL, and subsets of melanomas and carcinomas
Fontana-Masson
(+) melanin, Cryptococcus (has melanin pigment?), pigmented filamentous fungi (black), argentaffin granules/cells (black)
Forkhead box protein L2 (FOXL2)
Sensitive and specific marker for sex cord and stromal tumors of the ovary
(GATA-binding protein) GATA3
(+) bladder , poor px in invasive breast ca (is sens and specific for primary breast ca up to 94% sens, making it better than mammaglobin and GCDFP-15)
Giemsa
(+) RBCs (pink), starch/cellulose (sky blue), nuclei (blue), Helicobacter (dark blue)
- used in blood smears
Glial Fibrillary Astrocytic Protein (GFAP)
(+) glial (astros, oligodendros, ependymals), astrocytomas, oligodenrogliomas, ependymomas, also schwann cells
- also (+) in Rosenthal fibers and eosinophilic granular bodies
- negative: non-gliomas (carcinomas, melanomas, sarcomas)
-
Gross Cystic Disease Fluid Protein (GCDFP)-15
(+) apocrine cells, breast (1/2) - 5/5 LCIS's, breast mets, salivary / sweat glands, lung ca, lung, prostate
- cytoplasmic, high sens (7/10) and spec (19/20), ab to BRST-2
- used c ER/PR?
GLUT1
IHC: (+) Thymic ca, mesothelioma, infantile capillary hemangiomas (that slowly regress by scar formation)
- neg: thymoma, non-thymic ca (var), reactive mesothelium
Glutamine Synthetase
Normally stains rim of hepatocytes around central vein
- in Focal Nodular Hyperplasia stains in an irregular map-like pattern
- diffuse staining pattern seen in hepatic adenoma and HCC
Glypican-3
(+) hepatocellular ca
- neg: cholangioca, b9 liver nodules
(Gomori's?) Grocott's Methenamine Silver (GMS)
(+) all fungi, even Pneumocystis, Actinomyces, Nocardia and some encapsulated bacteria, elastic fibers, sutures, calcifications
- black
Gram-Weigert
(+) Gram + bacteria and PCP (blue/purple), acid-fast bugs (low sens)
- neg: gram negs (ordered c Brown & Hopps)
Granzyme B
(+) NK-cells
H3K27ME3
(+) Synovial sarcoma; nuclear expression in 1/2 of MPNST (esp high-grade MPNST)
neg:
Hale's Colloidal Iron
(+) chromophobe RCC, apical blush in oncocytoma (usually negative), sialomucins (salivary, sm and lg bowel), sulfamucins (lg bowel), hyaluronic acid (stromal myxoid mucin), mesothelioma
- neg: neutral mucin (prostate, gastric foveolar cells), adenoca, CC and papillary RCC
- does not stain iron (just a part of the stain)
HAM56
(+) monocytes / histiocytes
h-caldesmin
(+) smooth muscle tumors (LM, LMS)
- negative: myofibroblasts, endometrial stromal tumors of the uterus, UTROSCT, fibromatosis
- smooth muscle marker, cyto
HepPar1
(+) Liver (Cytoplasmic granlar reactivity), hepatocellular ca (specific)
- neg: cholangioca, metastatic adenoca
HER2
(+) overexpressed in up to 1/3 breast ca's (usually those less well-differentiated), also in lung and gyn ca
- negative: rare in normal breast
- membranous, prognostic in breast ca, monitors Herceptin tx, a growth factor receptor
-- call neg if <30% or only partial membrane staining, 2+ is weak but complete membrane staining in >30%, and 3+ strong complete stain in >30% of nuclei
--- weakly pos or equivocal cases get HER2 FISH/CISH (called "amplified" if >6 HER2 gene copies per nucleus or FISH ratio [HER2 gene signals to cr 17 signals] > 2.2; "HER2 non-amplified" if <4 genes/nuc or ratio <1.8
- well-differentiated tumors are ER/PR+, HER2 neg
Px: poor prognostic factor
HLA-DR
MHC class II, is a hallmark of immature hematopoietic cells; major role is to present exogenous peptides to T-cells that will recognize an antigen's epitope if the MHC molecular groove (although antigen presenting does not occur in immature cells) [1]
(+) antigen-presenting cells, B-cells, also activated T-cells, keep this marker past immature state normally
(+) B-ALL/LBL
-neg T cell dz and plasma cell neoplasms
HNF-1beta
(+) Ovarian and endometrial clear cell ca, some non-clear cell endometrial ca's
- neg: endometrioid ca, serous ca
human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
(+) choriocarcinoma (in syncytiotrophoblasts)
Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) - G
(+) trophoblastic cells (CT, ST, IT)
Human Melanoma, Black (HMB)-45
(+) epithelioid melanoma (6/10), normal melanoma (patchy and scattered pos), immature melanocytes, blue cell nevus (diffusely pos), conventional nevocellular nevi, junctional nests, papillary dermal nests, adnexal structure nests, PEComa, pheochromocytomas, gliosarcomas, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, clear cell "sugar" tumor
- negative: spindle cell and desmoplastic melanomas, mature melanocytes
- recognized gp100 protein (in premelanosomes), less sensitive but more specific (than MelanA/S100), more prominent at originating site of tumor where melancytes most immature, in nevi cells mature towards base and become HMB-45 neg
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV, by ISH)
(+) SCC / HSIL of cervix, anus and tonsils
- neg: atypical immature metaplasia and normal squamous mucosa
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL)
(+) choriocarcioma (in intermediate trophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts), exaggerated placental site, placental site trophoblastic tumor
- neg: placental site nodule (var), epithelioid trophoblastic tumor (var)
IgG4
(+) Plasma cells in lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing (autoimmune) pancreatitis
- neg:
- need >50 IgG4+ plasma cells per hpf to dx
IgM
(+) primary cutaneous DLBCL leg type (cytoplasmic), primary cutaneous mantle zone lymphoma (var)
- neg: primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma
Inhibin
(+) adrenal, sex cord stromal tumors, granular cell tumor, trophoblastic cells (ST, CT, IT), hemangioblastoma
Integrase Interactor 1 (INI1)
- aka SMARCB1 and hSNF5
Expression is lost in AT/RT, rhabdoid tumors, epithelioid sarcoma (conventional and proximal types), renal medullary carcinomas, a subset of epithelioid MPNST (2/3), myoepithelial carcinoma, extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (if has rhabdoid features)
Is a member of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex on cr 22q11.2
Insulinoma associated protein 1 (INSM1)
Nuclear marker of neuroendocrine differentiation, better sensitivity / specificity than CHR / SYN / CD56
- expressed in neuroendocrine tissue, neuroendocrine tumors, and developing neurons
Iron
(+) ferric iron in tissue sections, increased in hemochromatosis and hemosiderosis
Kappa
(+) monotypic in primary cutaneous MZL and DLBCL leg type,
- not monotypic in primary cutaneous Follicle center lymphoma
Kinyoun's
(+) acid-fast bacteria
- modified Ziel-Neelsen
Ki67
Nuc, non-histone nuclear protein expressed in in G1, S, G2, and M phases of cell cycle and rapidly catabolized at end of M phase and not detectable in G0 and early G1 cells [2]
- Ki67 was originally developed only for frozen tissue, MIB1 was later developed for paraffin-embedded tissue [2]
(+) proliferating cells, small cell carcinoma (70%), typical carcinoid (~1%, should be <2%), atypical carcinoid (10%, up to 20%), extends up to the surface in HSIL of cervix, choriocarcinoma (>50%)
- negative: atypical immature metaplasia (normal squamous mucosa of cervix; <10% usually; adenoca has >30% [not a rule])
- nuclear,
Latent Membrane Protein (LMP)
(+) Extranodal NK/T-cell lymhpoma nasal type
Leder
- aka Chloroacetate esterase (CAE)
(+) Neutros, mast cells and their precursor cells; also + in neoplastic but not normal eos
Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP)
Hydrolyzes napthol AS-bisphosphonate, in neut granules, forming colored product
- LAP score determined by counting 100 bands and neuts (each cell scored 0-4+, and sum of 100 cells added)
- Normal adults = 40-120
CML = 0-15
PNH, some MDSs, congenital hypophosphatasia, and neonatal septicemia (LAP score paradoxically dec) have low LAP score
- high LAP score in reactive conditions, PV, PMF, steroid use, 3rd tri preg
Lysozyme
(+) Monocytes / histiocytes
Lipase
(+) serous acinar cell (pancreas), pancreatoblastoma
- negative:
-
mammoglobin
cytoplasmic, maybe more sensitive than GCDFP (also in ~1/2 breast ca's), but not specific (stains gyn tumors other than breast [gyn, sweat / salivary glands])
Masson's Trichrome
(+) collagen (blue), muscle (red), Reinke crystals in Leydig cell tumor
- in kidney, can help to identify fibrosis, insudates or hyalinosis, and large immune deposits
- neg: sm muscle
- used for medical liver / kidney
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (McPyV)
Movat's Pentachrome
(+) MPS-rich loose collagen (blue-green, indicated sub-acute process), dense collagen / fibrosis (yellow, chronic processes)
- neg
- used mostly in lung
Melan-A / Melanoma Antigen Recognized by T-cells (MART-1)
(+) epithelioid melanoma (8/10), normal melanocytes, spindly/desmoplastic (patchy or negative), steroid hormone receptors, sex cord stromal tumors, clear cell sarcoma (lower expression), PEComa, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, clear cell "sugar" tumor
- negative:
- Melan A is the ab to MART1
Mouse Double Minute 2 Homolog (MDM2) [and CDK4?]
Can be done as IHC or molecular methods (such as RT-PCR)
- not entirely specific for atypical lipomatous tumors (also pos in intimal sarcoma, pleomorphic RMS, some MPNST, and some MFS)
- negative in pleomorphic liposarcoma and myxoid liposarcoma
MIB1
(+) proliferating cells
- negative:
Micropthalmia Transcription Factor (MITF)
(+) normal intraepidermal melanocytes, epithelioid melanoma (8/10), not too good for spindle cell and desmoplastic melanomas, PEComa family, pulmonary sugaar tumor, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, macrophages in LNs,
- negative:
- nuclear,
MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2
nuclear DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes: MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 and EPCAM
- microsatellite instability either through promoter hypermethylation (silences gene expression, seen in sporadic colorectal ca [1/3 colorectal ca's]) or by germline mutation (as in Lynch sundrome / HNPCC [3% of colorectal ca's]) - 95% sens, 100% spec
-- if all (+), then no defective MMR by IHC; if MLH1/PMS2 neg then MLH1 is defective (9/10 sporadic loss [promoter hypermethylation] 1/10 germline mutation); if PMS2 neg, then probably PMS2 germline mutation; if MSH2 and MSH6 neg, then defective (germline mtation) MSH2; if only MSH6 neg then germline MSH6 mutation
- MicroSatellite Instability (MSI) done through PCR
-- MMR deficient / MSI-high have better px per stage, dont respond well to 5-FU, and are better treated c irinotecan
*** Think of them in pairs, with the lower one getting messed up first: SH's go together; MLH and PMS go together; abnormality in MLH -> PMS abnormality, MLH1 -> MLH6 abnormality ***
Mucin 1 (MUC1)
(+) PanIN, esophagus (Barrett's mucosa)
- neg: Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) pancreas, gastric cardia (intestinal metaplasia of the gastric cardia)
MUC2
(+) Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) pancreas, esophagus (Barrett's mucosa)
- neg: PanIN, gastric cardia (intestinal metaplasia of the gastric cardia)
MUC4
(+) Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) pancreas and PanIN, sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma (SEF), low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS)
- neg
Mucicarmine
(+) goblet cells (adenoca, mucoepidermoid ca), sialomucins (salivary, sm and lg bowel), sulfamucins (lg bowel), Cryptococcus capsule (red/blue)
- neg: neutral mucin (prostate, gastric foveolar cells), hyaluronic acid (myxoid stromal mucin)
Multiple Myeloma Oncogene-1 (MUM1)
(+) primary cutaneous DLBCL leg type, and grade 3 follicular lymphoma
- neg: primary cutaneous FCL and MZL
- responsible (along with IRF4) for down-regulating BCL6 in centrocytes and helping the transition to memory B-cells / plasma cells
Muscle-specific actin (MSA)
(+) skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and myoepithelial cells, myofibroblasts (sometimes), Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (tram-track appearance [peripheral cytoplasmic]), rhabdomyosarcoma
- negative:
- pan-muscle marker like desmin, cytoplasmic
MYC
Name from Avian virus Myelocytomatosis (v-myc) homology with cellular Myc (c-Myc), seen in various cancers; Muc proteins are transcription factors
- plays important role in germinal center formation
- MYC is upregulated on interaction of naive B cells with antigen and T cells by BCL6
- in normal reactive lymph nodes, MYC highlights some centrocytes in the light zone of the GC and is repressed in the dark zone
- however, MYC is re-induced in a subset of light-zone B-cells (centrocytes), allowing re-entry to the dark zone and maintenancy of the germinal center reaction
Myeloperoxidase (MPO)
Stains primary (azurophilic) granules of granulocytes and myeloblasts
- neg in very early blasts, lymphs, erythroblasts, MGKCblasts, most monoblasts (can have fine dusty positivity)
- degrades quick in wet specimens, stable in smears up to 1 mo
-- thus a negative MPO should not itself exclude AML
myo-D
(+) rhabdomyosarcoma (highly specific)
- negative:
- nuclear skeletal muscle marker (beware: nonspecific cytoplasmic staining may be interpreted as positive!!)
myogenin
(+) skeletal mscule, rhabdomyosarcoma (highly specific)
- negative:
- nuclear transcription factor (like myoD)
Napsin-A
(+) lung, cytoplasmic granular reactivity, (papillary) RCC, rare weak thyroid, non-mucinous adenoca lung
- neg: mucinous adenoca lung (var), SCC lung, small cell ca lung, carcinoid lung, mesothelioma
- a protease found in type II pneumocytes
Neuronal Nuclei (NeuN)
(+) neuronal (not as reliable for tumors), gangliocytoma, ganglioglioma, central neurocytoma (var)
- negative:
- nuclear
Neurofilament Proteins (NFP)
(+) in axons of neurofibroma and ganglioneuroma, neuroblastoma, paragangliomas/pheochromocytomas, some subsets of NE tumors, Merkel cell ca (perinuclear dot-like positivity)
- neg: schwannoma
- are a major component of the cytoskeleton of neurons and its axons
- detection is not so good in FFPE tissue, even c modern IHC methods and their abs
(NK3 Homeobox 1) NKX3.1
Neuron-specific enolase (NSE)
(+) neuroendocrine, astrocytoma, meningioma, schwannoma, carcinoid, Merkel cell ca, small cell ca
- negative:
- not as specific for NE stuff but is sensitive (aka Not-Specific Enolase***)
Nonspecific Esterase (NSE)
alpha-napthyl estaerase and alpha-napthyl butyrate esterase stain the monos but pretty nonspecific
- rxn can be inhibited c sodium fluoride (NaF)
OCT4 (POU5F1)
(+) seminoma (sens +spec), dysgerminoma, ITGCN, embryonal ca
- neg: yolk sac tumor, spermatocytic seminoma, chorioca, teratoma, sex chord stromal tumors
Oil red O
(+) fat, hemangioblastoma, Burkitt's (vacuoles), liposarc, sebaceous ca, fat emboli
- neg: RCC
- tissue must be fresh/frozen, not fixed
OSCAR
Another type of keratin??
p16
- (+) HGSIL, cervical adenoca (AIS), serous ca (strong, diffusely pos), scattered ciliated cells and reserve cells of normal endocervix, scattered cells in metaplastic conditions of cervix, marker for high-risk HPV infx in SCC of cervix
- neg: atypical squamous metaplasia, endometrioid ca,
- nuclear and cytoplasmic, marker of high-risk HPV-infx
- normally is a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor which inactivates CDK4/6 and prevents phosphorylation of retinoblastoma
p53
(+) Glandular dysplasia in the GI tract, apoptosis (prognostic), Dysplasia Assoc Lesion or Mass (DALM), mesothelioma, urothelial CIS (4/5), serous ca (strong, diffusely pos), tubal intraepithelial ca (TIC)
- negative: sporadic tubular adenoma (tho + in late dz), hepatocellular ca (var), b9 liver nodules, reactive mesothelium, normal / reactive urothelium, clear cell ca
- nuclear; tumor suppressor protein whose mutant form is overexpressed in lots of ca's, not very specific
p57 (KIP2)
(+) Partial mole, hydropic abortus
- neg: complete moles
p57 is paternally imprinted maternally expressed gene, thus it is expressed and detectable by IHC when maternal copy present (and is absent when maternal copy absent), which is why it is absent in complete moles
- normal p57 expression is strong nuclear staining in cytotrophoblasts, intermediate trophoblasts, intervillous trophoblast islands, and villous stromal cells (syncytiotrophoblasts are uniformly neg)
Exceptions:
- maternal los of maternal cr 11 may have lack of p57 staining
- CHMs with retained maternal cr 11 can also have p57+
p62
Seen in Mallory bodies in the liver
p63
(+) ME cells breast, bladder, basal cells prostate, salivary glands, intermediate cells of mucoepidermoid carcinoma, SCC lung, placental site nodules, epithelioid trophoblastic tumor, choriocarcinoma (in cytotrophoblasts)
- negative: myofibroblasts and sm muscle, basal cells absent in invasive prostate ca, non-mucinous adenoca lung (var), mucinous adenoca lung (var), small cell ca lung, carcinoid lung, mesothelioma lung, exaggerated placental site, placental site trophoblastic tumor
- nuclear
*** Prostate Panel: p63, CK903, Racemase)***
- basal cells (p63+ nucleus, CK903+ cytoplasm) present in b9/non-invasive lesions, absent if invades and acinar cells are Racemase negative in b9 and pos (cytoplasmic) if invasive
- present in myoepithelial cells in b9/non-invasive breast ca (lost ME cells if invasive)
p120
- membranous staining in DCIS, cytoplasmic in LCIS
p75 neurotrophin receprot (p75NTR)
Suggestive of MPNST
Proline Glutamic Acid and Leucin-Rich Protein (PELP1)
May be more sens than GATA3 in Triple Negative Breast Ca, esp in cases of mets
Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS)
(+) serous acinar cells, (acinic cell ca salivary glands), sialomucins (salivary, sm and lg bowel), sulfamucins (lg bowel), neutral mucin (prostate, gastric foveolar cells), fungi, lymphoblasts (have "block/rosemary bead" positivity), myeloblasts (diffuse granular staining)
- negative: clear cells in acinic cell ca (?), hyaluronic acid (myxoid stromal mucin)
- diastase digests glycogen, but mucin is resistant to digestion
(Paired Box Gene) PAX-2
(+) kidney , papillary and clear cell RCC, oncocytoma
- neg: chromophobe, medullary, collecting duct ca's
PAX5
(+) pan-B cell marker, rhabdomyosarcoma (if translocation pos), HL
- negative: T cell neopalsms and plasma cell neoplasms
- nuc
PAX-8
(+) Thyroid (papillary and follicular ca), anaplastic ca thyroid (3/4), renal cell carcinomas (>90%, broader than PAX2), gyn tract, b9 renal tubules, renal epithelial neoplasms (papillary and clear cell, chromophobe, medullary, collecting duct, clear cell and papillary RCCs, oncocytoma,) serous ca, B-lymphocytes
-- >90% of non-mucinous ovarian ca's are PAX8+, whereas only ~1/2 of mucinous cas are PAX8+
- neg: medullary ca (var), parathyroid ca's, mesothelioma, breast, all primary lung ca's (may be weak focal, but never strong diffuse)
- nuclear, used to differentiate ER/PR (+) tumors
PLAP
(+) seminoma, dysgerminoma, ITGCN, germ cell tumors, embryonal ca, yolk sac tumor, chorioca (var)
- neg: spermatocytic seminoma, teratoma, sex cord-stromal tumors, Placental Site Trophoblastic Tumors (PSTT)
PR
(+) normal and cancerous breast, metastatic breast ca (3/5), pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm (both are ER neg), meningioma (1/2+), serous ca (1/2+), endometriosis (glands and stroma), endometrioid ca (9/10+)
- negative: mesothelioma, clear cell ca
- nuclear, marks therapuetic response /px in breast ca
-- called positive if >1% nuclear staining (must have good controls)
- PR synthesis controlled by ER (ER-/PR+ probably false, ER+/PR- is uncommon)
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
Prostate , cytoplasmic, more specific, id met prostate ca
- also (+) in salivary gland tumors (salivary duct ca)
Prostate-specific acid phosphatase (PSAP)
Prostate , cytoplasmic, more sensitive, id met prostate ca
- also (+) in rectal carcinoid
Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA)
(+) prostate
- negative
- membranous
Prostein (P501S)
(+) prostate (sensitive and specific)
- negative
- cytoplasmic dot-like granular reactivity
PTAH
(+) oncocytoma and oncocytic ca (salivary glands)
PTH
Parathyroid
Racemase (P504S, AMACR)
(+) overexpression in prostate cancer cells, but also pos in adenosis (1/10), Papillary RCC (10/10), variably in clear cell RCC and nephrogenic adenoma (6/10)
- negative: benign prostate cells, but also neg in pseudohyperplastic ca, atrophic ca, and foamy ca
- granular cytoplasmic reactivity
*** Prostate Panel: p63, CK903, Racemase)***
- basal cells (p63+ nucleus, CK903+ cytoplasm) present in b9/non-invasive lesions, absent if invades and acinar cells are Racemase negative in b9 and pos (cytoplasmic) if invasive
RCC
Similar staining as CD10?; Older marker for RCC (not very sensitive or specific)
(+) Clear cell RCC (diffuse), var in papillary and chromophobe RCC
- neg: oncocytoma
Reticulin
(+) highlights thickened hepatocyte plates (>3 cells thick) in hepatocellular ca (vs normal thickness in b9 liver nodules),
- pericellular positivity: HPC, fibrosarcoma, schwannoma, PXA, lymphoma, sarcomatous areas of gliosarcoma
- nested: hemangioblastoma, pituitary (enlarged irreg lobules in adenoma vs sm nests in normal pit)
- neg: all gliomas (with the exception of PXA), SFT, meningioma, normal network lost in HCC (?see above?)
Rhodanine
(+) Copper [as in Wilson's dz
(Sal-Like Protein) SALL4
(+) pan germ cell marker (fairly spec), yolk sac tumors (neg OCT4), seminomas, ITGNC, spermatocytic seminomas, embryonal ca, leukemia cells, teratomas (var), chorioca (var), hepatoid gastric AC
- neg: sex cord-stromal tumors
- nuclear
Soluble in 100% (S100) ammonium sulfate
(+) Melanomas (>9/10, even spindly and desmoplastic), schwann cells, gliomas, lipocytes, nerve sheath tumors (neurofibroma, schwannoma, MPNST), granular cell tumor, MyoEpithelial ca's, histiocytes (LCH), chordoma, glioma, carcinomas (breast), clear cell sarcoma, granular cell tumor, fibrous meningioma (4/5), DNET, chordoma, myxoid chondrosarcoma (var), myxopapillary ependymoma (var), dendritic cells, cartilaginous tumors, neural crest tissues
- negative: NE cells (but does stain sustentacular cells in some NE tumors [pheo]), not too good at PEComa family (3/10 pos), synovial sarcoma (3/10), choroid meningioma
- nuclear and cytoplasmic, calcium binding protein, most sensitive melanocytic marker, low specificity
- present in myoepithelial cells in b9/non-invasive breast ca (lost ME cells if invasive)
Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1)
Sensitive and specific marker for sex cord and stromal tumors of the ovary
Sm32
(+) Neuronal cells, gangliocytoma, ganglioglioma, central neurocytoma
smooth muscle actin (SMA)
(+) smooth muscle, "railroad-tracks" in myofibroblasts, smooth muscle spindle cell tumors (LM, LMS, RMS), myofibroblastic spindle cell tumors (fibromatosis, nodular fascitis, IMT), some GISTS, ME cells breast, glomus tumor, UTROSCT (var)
- negative: skeletal muscle
- aka a-actin, cytoplasmic
- present in myoepithelial cells in b9/non-invasive breast ca (lost ME cells if invasive)
- false neg: microglandular adenosis lacks ME cells
- false pos: rare invasive ductal ca have ME cell foci
Smoothelin
(+) strong pos in muscularis propria (detrusor muscle)
- neg: muscularis mucosa (desmoplastic myofibroblasts, can be focal +)
SMAD4
aka DPC4 (?), lost in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
smooth muscle myosin heavy chain (SMMHC)
(+) ME cells breast, vessels, smooth muscle
- negative: skeletal muscle, myofibroblasts
- smooth muscle marker, cytoplasmic
- present in myoepithelial cells in b9/non-invasive breast ca
(Sex-Determining Region Y) SOX2
(+) Embryonal ca
- nuclear
SOX9
Cartilage differentiation
Sry-related HMG-BOX gene 10 (SOX10)
(+) melanoma (including desmoplastic and spindle cell), schwann cell tumors, clear cell sarcoma, astrocytomas, myoepithelial tumors, granular cell tumors, some breast carcinomas, relatively specific for neuroectodermal neoplasms, epithelioid MPNST
- neg: macrophages (more spec than MITF), scar
- nuclear stain for melanocytes and schwannian cells
- less likely to be expresed by background fibroblasts
SOX11
marker for mantle cell lymphoma, can be useful in cases of Cyclin-D1 negative MCL
- SOX11 positivity is relatively specific, can be positive in Burkitt lymphoma (25%) and in hairy cell leukemia (50%)
- may play a role in early neuronal development and maturation of neurons
absence of SOX11 expression in MCL may be indicative of an indolent MCL
90% of cases of Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) with nuclear positivity, including Cyclin D1 negative cases
- complicated story as a prognostic indicator - better px but dismal if also with TP53 abnormalities
- MRQ-58 antibody very specific but other ab that may still be used stain many lymphoblastic lymphomas, some BL, and some DLBCL
- SOX11 normally stains scattered positive cells in GC
(Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 6) STAT6
sensitive and specific marker for SFT
Overexpression of nuclear STAT6 results from NAB2-STAT6 fusion identified in SFTs
Succinate dehydrogenase B (SDHB)
Mitochondrial enzyme complex involved in the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain essential for normal aerobic respiration
- comprised of 4 subunits (SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD) and an assembly factor SDHAF2
- loss of SDHB may be indicative of syndromic disease; either with germline inactivation of any subunit or SDHC hypermethylation
- loss of SDHB seen in 15% of pheochromocytomas / paragangliomas, 3% of GISTs, and <1% of renal cell carcinomas and <1% of pituitary adenomas
Sudan black B
(+) fat (in heme will show in grans, c reactivity similar to MPO)
- tissue should be fresh/frozen and not fixed
Synaptophysin (SYN)
(+) neuroendocrine, medullary ca thyroid, parathyroid ca's, carcinoid, neuronal cells, gangliocytoma, ganglioglioma, central neurocytoma, medulloblastoma (also GFAP +), pineal neoplasms, choroid plexus tumors, Merkel cell ca, small cell ca
- negative: DNET, sertoli cell / granulosa cell tumors (var), endometrioid ca, struma ovarii
- more sensitive than CHR, cytoplasmic
Tau
Glial fibrillary tangles
TCL1
(+) CD4+/56+ hematodermic neoplasm / Plasmacytoid dendritic cell tumor
TdT
Marker of immature / thymic T-cells
IHC: (+) lymphs in thymoma, CD4+/56+ hematodermic neoplasm / Plasmacytoid dendritic cell tumor (var)
- neg: thymic ca, non-thymic ca
Transduction-like enhancer of split 1 (TLE1)
(+) Synovial sarcoma (85-97%), endometrial stromal sarcoma, SFT, MPNST, Ewing, schwannoma, epithelioid sarcoma
Is a transcriptional repressor essential to hematopoiesis, neuronal differentiation, and terminal epithelial differentiation
- also plays important role in synovial sarcoma-assoc Wnt/B-catenin signaling pathway
TFE3
(+) Alveolar soft parts sarcoma (nuclear), PEComa (some), epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE; a small subset is+) , lymphangioleiomyomatosis (1/10), clear cell "sugar" tumor (1/10)
- neg: anaplastic ca, medullary ca, parathyroid ca
Thyroglobulin
(+) Thyroid, papillary and follicular ca thyroid,
- neg: anaplastic ca, medullary ca, parathyroid ca
Transthyretin
(+) Choroid plexus tumors
Trypsin
(+) serous acinar cells, pancreatoblastoma
- negative:
-
TTF-1
(+) Lung (non-squamous), thyroid (medullary, papillary and follicular), desmoplastic small round cell tumor, hepatocellular ca (cytoplasmic), non-mucinous adenoca lung, small cell ca lung (9/10), carcinoid lung (1/3, weak), struma ovarii
- negative: parathyroid ca, anaplastic ca thyroid, mucinous adenoca lung (2/10+), SCC lung, mesothelioma lung, carcinoid tumor, endometrioid ca, sertoli cell tumor / granulosa cell tumor, Merkel cell ca
- nuclear
Type IV Collagen
(+) Glomus tumor (pericellular)
Ubiquitin
Normally pathway for protein degradation assoc c turning on and off cell cycle regulators; can turn on cyclin-CDK complexes by destroying its inhibitor
- may stain neuronal inclusions in motor neuron disease
uroplakin
(+) Bladder
villin
(+) hepatocellular ca (canalicular)
- neg: cholangioca
vimentin
(+) RCC (clear cell and papillary types), endometrium, mesothelioma, salivary gland, thyroid, sweat gland, spindle cell carcinomas
- negative: RCC (chromophobe and oncocytoma), adenoca of endocervix, lung ca, breast, ovary, prostate, colorectal ca, HCC
- mesenchymal marker, though not specific for mesenchymal cells
- type II intermediate filament protein encoded by VIM gene
Verhoerff's Van Gieson (VVG or Elastic stain)
(+) thinned elastic tissue in emphysema, lost in some vascular dz
- neg
- used to evaluate vessels and invasion of elastica in visceral pleura in pulmonary ca staging
Von Kossa
(+) calcium
- neg: urate crystals
Warthin's Starry silver
(+) Helicobacter, spirochetes, Chlamydia, Legionella
Wilms Tumor 1 (WT1) protein
(+) mesothelioma, ovarian serous carcinoma, Wilms tumor, desmoplastic small round cell tumor, mesothelium (b9 and cancerous),
- negative: endometrial serous ca (var), endometrioid ca, clear cell ca
- nuclear,
ZAP-70
normally in T and NK cells; seen in some CLL/SLL, B-ALL, most T cell cancers
- positivity in CLL/SLL means unmutated IgVH and aggressive course


References
1. Porwit. Multiparameter Flow Cytometry in the Diagnosis of Hematologic Malignancies. 2018
2. Schwaring et al. CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders as Potential Candidates for CD30-Targeted Therapies. Ach Pathol Lab Med. 2022; 146:415-432.
